College Algebra
Answer/Discussion to Practice Problems
Tutorial 23B: Rational Inequalities
 Answer/Discussion
to 1a Answer/Discussion
to 1a
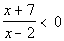
I used the test-point method, but you could also use the sign graph of
factors method.
|
This quadratic inequality is already in standard form. |
Step 2: Factor the numerator
and denominator and find the values of x that make these
factors
equal to 0 to find
the boundary
points. |
|
*Set numerator = 0 and solve
|
|
*Set denominator = 0 and solve |
-7 and 2 are boundary points. |
Below is a graph that marks off the boundary points -7
and 2 and shows
the three sections that those points have created on the graph.
Note
that open holes were used on those two points since our original
inequality
did not include where it is equal to 0 and 2 makes the denominator
0.

Note that the two boundary points create three sections
on the graph: 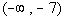 , , 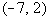 , and , and 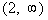 . . |
You can choose ANY point in an interval to represent
that interval.
Remember that we are not interested in the actual value that we get,
but
what SIGN (positive or negative) that we get.
Keep in mind that our original problem is 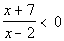 .
Since we are looking for the quadratic expression to be LESS
THAN 0, that means we need our sign to be NEGATIVE. .
Since we are looking for the quadratic expression to be LESS
THAN 0, that means we need our sign to be NEGATIVE.
From the interval 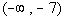 ,
I choose to use -8 to test this interval: ,
I choose to use -8 to test this interval:
(I could have used -10, -25, or -10000 as long as it is in the interval) |
|
*Chose -8 from 1st interval to
plug in for x
|
Since 1/10 is positive and we are looking for values
that cause
our quadratic expression to be less than 0 (negative), 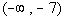 would
not be part of the solution. would
not be part of the solution. |
From the interval 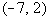 ,
I choose to use 0 to test this interval. ,
I choose to use 0 to test this interval.
(I could have used -6, -5, or -4 as long as it is in the interval) |
|
*Chose 0 from 2nd interval to
plug in for x
|
Since -7/2 is negative and we are looking for values
that cause
our expression to be less than 0 (negative), 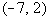 would be part of the solution. would be part of the solution. |
From the interval 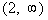 ,
I choose to use 3 to test this interval. ,
I choose to use 3 to test this interval.
(I could have used 10, 25, or 10000 as long as it is in the interval) |
|
*Chose 3 from 3rd interval to
plug in for x
|
Since 10 is positive and we are looking for values
that cause our
quadratic expression to be less than 0 (negative), 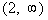 would not be part of the solution. would not be part of the solution. |
Interval notation: 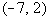
Graph:
 |
*Open interval indicating all
values between
-7 and 2
*Visual showing all numbers
between -7 and
2 on the number line
|
 Answer/Discussion
to 1b Answer/Discussion
to 1b
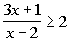
I used the test-point method, but you could also use the sign graph of
factors method.
|
|
*Inv. of add. 2 is sub. 2
*Rewrite 2nd fraction with LCD
of x - 2
|
Step 2: Factor the numerator
and denominator and find the values of x that make these
factors
equal to 0 to find
the boundary
points. |
|
*Set numerator = 0 and solve |
|
*Set denominator = 0 and solve |
-5 and 2 are boundary points. |
Below is a graph that marks off the boundary points -5
and 2 and shows
the three sections that those points have created on the graph.
Note
that there is an open hole at -2. Since that is the value that
cause
the denominator to be 0, we cannot include where x = 2. Since our inequality includes where it is equal to 0, and -5
causes only the numerator to be 0 there is a closed hole at -5.

Note that the two boundary points create three sections
on the graph: 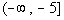 , , 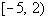 ,
and ,
and 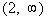 . . |
You can choose ANY point in an interval to represent
that interval.
Remember that we are not interested in the actual value that we get,
but
what SIGN (positive or negative) that we get.
Keep in mind that our inequality is 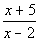 > 0. Since we are looking for the quadratic expression to be GREATER
THAN OR EQUAL TO 0, that means we need our sign to be POSITIVE
(OR O). > 0. Since we are looking for the quadratic expression to be GREATER
THAN OR EQUAL TO 0, that means we need our sign to be POSITIVE
(OR O).
From the interval 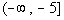 ,
I choose to use -6 to test this interval: ,
I choose to use -6 to test this interval:
(I could have used -10, -25, or -10000 as long as it is in the interval) |
|
*Chose -6 from 1st interval to
plug in for x
|
Since 1/8 is positive and we are looking for values
that cause our
quadratic expression to be greater than or equal to 0 (positive or
0), 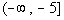 would be part of the solution. would be part of the solution. |
From the interval 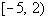 ,
I choose to use 0 to test this interval. ,
I choose to use 0 to test this interval.
(I could have used -4, -3, or -2 as long as it is in the interval) |
|
*Chose 0 from 2nd interval to
plug in for x
|
Since -5/2 is negative and we are looking for values
that cause
our expression to be greater than or equal to 0 (positive or 0), 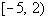 would
not be part of the solution. would
not be part of the solution. |
From the interval 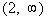 ,
I choose to use 3 to test this interval. ,
I choose to use 3 to test this interval.
(I could have used 10, 25, or 10000 as long as it is in the interval) |
|
*Chose 3 from 3rd interval to
plug in for x
|
Since 8 is positive and we are looking for values
that cause our
quadratic expression to be greater than or equal to 0 (positive or
0), 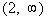 would
be part of the solution. would
be part of the solution. |
Interval notation: 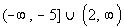
Graph:
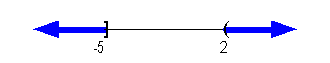 |
*An closed interval indicating
all values
less than or equal to -5 and an open interval indicating
all
values greater then 2
*Visual showing all numbers
less than or equal
to -5 and indicating all values greater then 2
|

Last revised on Jan. 2, 2010 by Kim Seward.
All contents copyright (C) 2002 - 2010, WTAMU and Kim Seward. All rights reserved.
|
|


