Intermediate Algebra
Tutorial 24: Exponents and Scientific Notation, Part II
|
WTAMU > Virtual Math Lab > Intermediate Algebra
 Learning Objectives Learning Objectives
After completing this tutorial, you should be able to:
- Simplify exponential expressions involving raising a base to two
exponents,
raising a product to an exponent and raising a quotient to an
exponent.
- Multiply and divide numbers written in scientific notation.
|
 Introduction Introduction
This tutorial picks up where Tutorial
23: Exponents and Scientific Notation Part I left off. It
finishes the rules of exponents with raising a base to two exponents,
raising
a product to an exponent and raising a quotient to an exponent.
Also
we will revisit the concept of scientific notation. Like it or
not,
the best way to master these exponents is to work through exponent
problems.
So I guess we better get to it.
|
 Tutorial Tutorial
Base Raised to Two Exponents
Specific Illustration
|
|
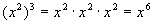
Note how 2 times 3 is 6, which is the exponent of the
final answer.
We can think of this as 3 groups of 2, which of course would come out
to
be 6. |
Base Raised to two Exponents
in general,
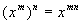
|
In other words, when you
raise a base to two
exponents, you multiply those exponents together.
Again, you can think of it as n groups of m if it helps you to remember.
 Example
1: Simplify Example
1: Simplify 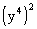 . .
|
|
*When raising a base to 2
powers you mult.
your exponents |
A Product Raised to an Exponent
Specific Illustration
|
|
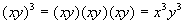
Note how both bases of your product ended up being
raised by the exponent
of 3. |
A Product Raised to an Exponent
in general,
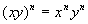
|
In other words, when you have
a PRODUCT (not
a sum or difference) raised to an exponent, you can simplify by raising
each base in the product to that exponent.
 Example
2: Simplify Example
2: Simplify 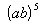 . .
|
|
*When raising a product to an
exponent, raise
each base of the product to that exponent |
A Quotient Raised to an Exponent
Specific Illustration
|
|
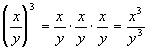
Since, division is really multiplication of the
reciprocal, it has the
same basic idea as when we raised a product to an exponent. |
A Quotient Raised to an Exponent
in general,
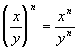
|
In other words, when you have
a QUOTIENT (not
a sum or difference) raised to an exponent, you can simplify by raising
each base in the numerator and denominator of the quotient to that
exponent.
 Example
3: Simplify Example
3: Simplify 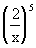 . .
|
|
*When raising a quotient to an
exponent, raise
each base of the quotient to that exponent
*Use def. of exponents to
evaluate |
Of course, we all know that life isn’t so cut and
dry. A lot
of times you are needing to use more than one definition or law of
exponents
to get the job done. What we did above and in Tutorial
23: Exponents and Scientific Notation Part I was to set the
foundation
to make sure you have a good understanding of the different ideas
associated
with exponents. Next we will work through some problems which
will
intermix these different laws. |
 Example
4: Example
4: Simplify. Use positive exponents to
write
the answer.
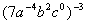 |
 Example
5: Example
5: Simplify. Use positive exponents to
write
the answer.
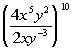 |
 Example
6: Example
6: Simplify. Use positive exponents to
write
the answer.
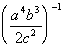 |
Not quite finished. Remember that the number has
to be between
1 and 10 for it to be in scientific notation. |
 Practice Problems Practice Problems
These are practice problems to help bring you to the
next level.
It will allow you to check and see if you have an understanding of
these
types of problems. Math works just like
anything
else, if you want to get good at it, then you need to practice
it.
Even the best athletes and musicians had help along the way and lots of
practice, practice, practice, to get good at their sport or instrument.
In fact there is no such thing as too much practice.
To get the most out of these, you should work the
problem out on
your own and then check your answer by clicking on the link for the
answer/discussion
for that problem. At the link you will find the answer
as well as any steps that went into finding that answer. |
 Practice
Problems 1a - 1c: Simplify, use positive exponents to
write each answer. Practice
Problems 1a - 1c: Simplify, use positive exponents to
write each answer.
 Practice
Problems 2a - 2b: Perform indicated operations,
write each result
in scientific notation. Practice
Problems 2a - 2b: Perform indicated operations,
write each result
in scientific notation.
 Need Extra Help on these Topics? Need Extra Help on these Topics?

Last revised on July 12, 2011 by Kim Seward.
All contents copyright (C) 2001 - 2011, WTAMU and Kim Seward. All rights reserved.
|


