College Algebra
Tutorial 43: Logarithmic Functions
 Learning Objectives Learning Objectives
After completing this tutorial, you should be able to:
- Know the definition of a logarithmic function.
- Write a log function as an exponential function and vice versa.
- Graph a log function.
- Evaluate a log.
- Find the domain of a log function.
|
 Introduction Introduction
In this tutorial we will be looking at logarithmic functions.
If you understand that A LOG IS ANOTHER WAY TO
WRITE AN EXPONENT, it will help you tremendously when you work
through the various types of log problems. One thing that I will
guide you through on this page is the definition of logs. This is
an important concept to have down. If you don't have it down it makes
it hard to work through log related problems. I will also take you
through graphing, evaluating and finding the domain of logs. I think
you are ready to get started. |
 Tutorial Tutorial
IN OTHER WORDS - AND I CAN NOT STRESS THIS ENOUGH- A
LOG IS ANOTHER WAY TO WRITE AN EXPONENT.
This definition can work in both directions. In some cases you
will have an equation written in log form and need to convert it to exponential
form and vice versa.
So, when you are converting from log form to exponential form, b is your base, Y IS YOUR EXPONENT, and x is what your exponential expression is set equal to.
Note that your domain is all positive real numbers and range is all
real numbers. |
 Example
1 Example
1: Express the logarithmic equation 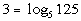 exponentially. |
We want to use the definition that is above: 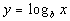
if and only if 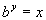 .
First, let's figure out what the base needs to be. What do you
think? It looks like the b in the definition
correlates with 5 in our problem - so our base is going to be 5.
Next, let's figure out the exponent. This is very key, again remember
that logs are another way to write exponents. This means the log
is set equal to the exponent, so in this problem that means that the exponent
has to be 3.
That leaves 125 to be what the exponential expression is set equal
to.
Putting all of this into the log definition we get: |
|
*Rewriting in exponential form |
Hopefully, when you see it written in exponential form you can tell
that it is a true statement. In other words, when we cube 5 we do
get 125. If you had written as 5 raised to the 125th power, hopefully
you would have realized that was not correct because it would not equal
3. |
 Example
2 Example
2: Express the logarithmic equation 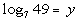 exponentially. |
We want to use the definition that is above: 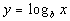
if and only if 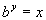 .
First, let's figure out what the base needs to be. What do you
think? It looks like the b in the definition
correlates with 7 in our problem - so our base is going to be 7.
Next, let's figure out the exponent. This is very key, again remember
that logs are another way to write exponents. This means the log
is set equal to the exponent, so in this problem that means that the exponent
has to be y.
That leaves 49 to be what the exponential expression is set equal
to.
Putting all of this into the log definition we get: |
|
*Rewriting in exponential form |
 Example
3 Example
3: Express the exponential equation 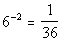
in a logarithmic form. |
This time I have you going in the opposite direction we were going
in examples 1 and 2. But as mentioned above, you can use the log
definition in either direction. These examples are to get you use
to that definition: 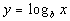
if and only if 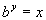 .
First, let's figure out what the base needs to be. What do you
think? It looks like the b in the definition
correlates with 6 in our problem - so our base is going to be 6.
Next, let's figure out the exponent. In this direction it is easy
to note what the exponent is because we are more used to it written in
this form, but when we write it in the log form we have to be careful to
place it correctly. Looks like the exponent is -2, don't you
agree?
The value that the exponential expression is set equal to is what
goes inside the log function. In this problem that is 1/36.
Let's see what we get when we put this in log form: |
 Example
4 Example
4: Express the exponential equation 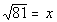
in a logarithmic form. |
Again we are going in the opposite direction we were going in examples
1 and 2. But as mentioned above, you can use the log definition in
either direction. These examples are to get you use to that definition: 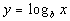
if and only if 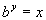 .
Rewriting the original problem using exponents we get:
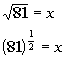
First, let's figure out what the base needs to be. What do you
think? It looks like the b in the definition
correlates with 81 in our problem - so our base is going to be 81.
Next, let's figure out the exponent. In this direction it is easy
to note what the exponent is because we are more used to it written in
this form, but when we write it in the log form we have to be careful to
place it correctly. Looks like the exponent is 1/2, don't
you agree?
The value that the exponential expression is set equal to is what
goes inside the log function. In this problem that is x.
Let's see what we get when we put this in log form: |
Step 1: Set
the log equal to x. |
This will give you a form that you are more familiar with. |
Whenever you are finding a log, keep in mind that logs
are another way to write exponents. You can always
use the definition to help you evaluate.
Let's step through a few examples of this: |
 Example
5 Example
5: Evaluate the expression 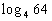 without
using a calculator. |
When we are looking for the log itself, keep in mind that logs are
another way to write exponents.
The thought behind this is, we are wanting the power that we would
need to raise 4 to to get 64. |
Step 1: Set
the log equal to x
AND |
Step 2: Use the definition
of logs shown above to write the equation in exponential form
AND |
|
*Setting the log = to x
*Rewriting in exponential form
*x is the exponent
we need on 4 to get 64 |
So the exponent we were looking for is 3. |
 Example
6 Example
6: Evaluate the expression 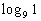 without
using a calculator. |
When we are looking for the log itself, keep in mind that logs are
another way to write exponents.
The thought behind this is, we are wanting the power that we would
need to raise 9 to to get 1. |
Step 1: Set
the log equal to x
AND |
Step 2: Use the definition
of logs shown above to write the equation in exponential form
AND |
|
*Setting the log = to x
*Rewriting in exponential form
*x is the exponent
we need on 9 to get 1 |
So the exponent we were looking for is 0. |
 Example
7 Example
7: Evaluate the expression 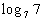 without
using a calculator. |
When we are looking for the log itself, keep in mind that logs are
another way to write exponents.
The thought behind this is, we are wanting the power that we would
need to raise 7 to to get 7. |
Step 1: Set
the log equal to x
AND |
Step 2: Use the definition
of logs shown above to write the equation in exponential form
AND |
|
*Setting the log = to x
*Rewriting in exponential form
*x is the exponent
we need on 7 to get 7 |
So the exponent we were looking for is 1. |
 Example
8 Example
8: Evaluate the expression 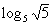 without
using a calculator. |
When we are looking for the log itself, keep in mind that logs are
another way to write exponents.
The thought behind this is, we are wanting the power that we would
need to raise 5 to get square root of 5. |
Step 1: Set
the log equal to x
AND |
Step 2: Use the definition
of logs shown above to write the equation in exponential form
AND |
|
*Setting the log = to x
*Rewriting in exponential form
*x is the exponent
we need on 5 to get square root of 5 |
So the exponent we were looking for is 1/2. |
You have to be careful that you note that the log key on your calculator
is only for base 10 and your ln key is only for base e.
So if you have any other base, you would not be able to use your calculator.
But, if you have it written in exponential form, you can enter in any base
in your calculator - that is why we do step 1. |
Step 2: Plug in
values for y (NOT x) to find some ordered pairs. |
Note that this is what we call an inverse function of the exponential
function. If you need a review of exponential functions feel free
to go to Tutorial 42: Exponential
Functions. They are inverses because there x and y values are switched. In the exponential
functions the x value was the exponent, but
in the log functions, the y value is the exponent.
The y value is what the exponential function
is set equal to, but in the log functions it ends up being set equal to x.
So that is why in step 2, we will be plugging in for y instead of x. |
This is done exactly the same way you plot points for any other graph. |
The basic curve of a log function looks like
the following: |
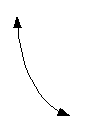
|
OR
|
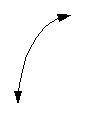
|
 Example
9 Example
9: Graph the function 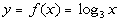 . |
First, we need to write in exponential form, just like we practiced
in examples 1 and 2.
Looks like the base is 3, the exponent is y,
and the log will be set = to x: |
|
*Rewriting in exponential form
|
Step 2: Plug in
values for y (NOT x) to find some ordered pairs. |
Step 3: Plot points.
AND
Step 4: Draw a curve. |
 Example
10 Example
10: Graph the function 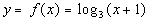 . |
First, we need to write in exponential form, just like we practiced
in examples 1 and 2.
Looks like the base is 3, the exponent is y,
and the log will be set equal to x + 1: |
|
*Rewriting in exponential form
|
Step 2: Plug in
values for y (NOT x) to find some ordered pairs. |
Step 3: Plot points.
AND
Step 4: Draw a curve. |
 Example
11 Example
11: Graph the function  . |
Setting this up to be able to use the definition we get:
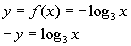
Next, we need to write in exponential form, just like we practiced in
examples 1 and 2.
Looks like the base is 3, the exponent is -y,
and the log will be set equal to x: |
|
*Rewriting in exponential form
|
Step 2: Plug in
values for y (NOT x) to find some ordered pairs. |
Step 3: Plot points.
AND
Step 4: Draw a curve. |
 Example
12 Example
12: Find the domain of the logarithmic function 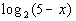 . |
|
Since x is part of the inside of the log
on this problem we need to find a value of x,
such that the inside of the log, 5 - x, is
positive. |
|
*Inside of log must be positive
*Solve the inequality
*Domain of this function |
The domain is x < 5.
That means that if we put in any value of x that is less than 5, we will end up with a positive value inside our log. |
 Example
13 Example
13: Find the domain of the logarithmic function 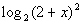 . |
|
Note how on this problem the inside of the log is squared. So
no matter what we plug in for x, the inside
will always be positive or zero. Since we can only have positive
values inside the log, our only restriction is where the inside would
be 0. |
|
*Inside of log cannot equal 0
*Domain of this function |
The domain is all real numbers except -2. |
|
Inverse Properties of Logarithms
|
|
Inverse Property I
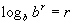 , ,
where b > 0 and b is not equal to 1.
|
Basically, what we are saying here is, whenever the base of your log
matches with the base of the inside of your log, then the log will equal
the exponent of the inside base - but only if the bases match!!!
Boy, the definition of logs sure does come
in handy to explain these properties - applying that definition you would
have b raised to the r power which equals b raised to the r power.
Here is a quick illustration of how this property works:
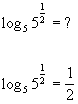
|
|
Inverse Property II
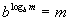 , ,
where b > 0 and b is not equal to 1.
|
Basically, what we are saying here is, whenever you have a base raised
to a log with the SAME base, then it simplifies to be whatever is inside
the log.
This one is a little bit more involved and weird looking huh?
Going back to our favorite saying - a log is another way to write exponents
- what we have here is the log is the exponent we need to raise b to get m, well if we turn around an raise our
first base b to that exponent, it stands to
reason that we would get m.
Here is a quick illustration of how this property works:
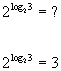
|
|
Common Log
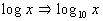
|
In other words, if no base is written for the log, it is understood
to be base 10, which is called the common log.
When using common log (base 10), use the form log x to write it. |
|
Natural Log
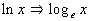
|
In other words, if the log is written with ln, instead of log in
front of the x, then it is understood to be
a log of base e, which
is called the natural log.
When using the natural log (base e),
use the form ln x to write it. |
 Example
14 Example
14: Evaluate 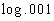 without the use of a calculator. |
We can either use the definition of logs, as shown above, or the inverse
properties of logs to evaluate this.
I'm going to use the first inverse property shown above: |
|
*Rewrite .001 as 10 to the -3rd power
|
 Example
15 Example
15: Evaluate 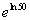 without the use of a calculator. |
 Example
16 Example
16: Simplify 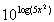 without
the use of a calculator. |
 Example
17 Example
17: Simplify 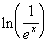 without
the use of a calculator. |
 Practice Problems Practice Problems
These are practice problems to help bring you to the next level.
It will allow you to check and see if you have an understanding of these
types of problems. Math works just like anything
else, if you want to get good at it, then you need to practice it.
Even the best athletes and musicians had help along the way and lots of
practice, practice, practice, to get good at their sport or instrument.
In fact there is no such thing as too much practice.
To get the most out of these, you should work the problem out on
your own and then check your answer by clicking on the link for the answer/discussion
for that problem. At the link you will find the answer
as well as any steps that went into finding that answer. |
 Practice Problems 1a - 1b: Express the given logarithmic equation exponentially. Practice Problems 1a - 1b: Express the given logarithmic equation exponentially.
 Practice Problems 2a - 2b: Express the given exponential equation in a logarithmic
form. Practice Problems 2a - 2b: Express the given exponential equation in a logarithmic
form.
 Practice Problems 3a - 3d: Evaluate the given log function without using
a calculator. Practice Problems 3a - 3d: Evaluate the given log function without using
a calculator.
 Practice Problems 4a - 4b: Graph the given function. Practice Problems 4a - 4b: Graph the given function.
 Practice Problem 5a: Find the domain of the given logarithmic function. Practice Problem 5a: Find the domain of the given logarithmic function.
 Practice Problems 6a - 6b: Evaluate the given expression without the use
of a calculator. Practice Problems 6a - 6b: Evaluate the given expression without the use
of a calculator.
 Practice Problems 7a - 7b: Simplify the given expression without the use of a
calculator. Practice Problems 7a - 7b: Simplify the given expression without the use of a
calculator.
 Need Extra Help on these Topics? Need Extra Help on these Topics?

Last revised on March 22, 2011 by Kim Seward.
All contents copyright (C) 2002 - 2011, WTAMU and Kim Seward. All rights reserved.
|
|


